The Different Types of Eczema – Which One Do You Have?
Dry, sore and itchy, eczema causes discomfort to millions of people worldwide. While it may seem to look the same, there are actually different types of eczema presenting in various forms, each with specific symptoms and triggers.
Read on as we explore the 7 different types of eczema, identify what causes this condition and discuss effective eczema treatment options so you can feel comfortable and confident in your skin.
All About Eczema
Eczema, professionally known as atopic dermatitis, is more than just dry skin or an occasional rash. It’s a highly complex, chronic inflammatory skin condition characterised by itchy, inflamed skin that becomes red, swollen and painful.
While it most commonly appears in children, different types of eczema affect adults, impacting their quality of life due to the way it looks and constant irritation.
So, what is eczema?
Eczema is an immune response causing skin inflammation. But some other factors, including genetics, environmental triggers and skin barrier dysfunction, also playing a role. The skin barrier, which is supposed to protect from microbes and allergens, doesn’t work as well when you have eczema, allowing moisture to escape and allergens and irritants to enter, leading to flare-ups. Luckily there are plenty of eczema treatments available to help relieve some of the worst symptoms.
Common eczema symptoms
- Persistent itching, which can be severe and often worsens at night.
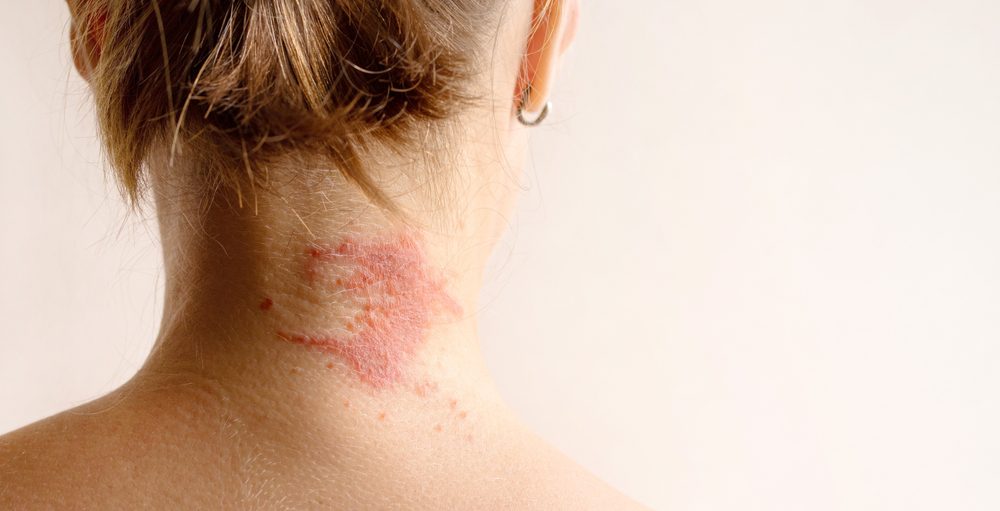
- Red or brownish-grey patches, especially on the hands, feet, ankles, wrists, neck, upper chest, eyelids, inside the bend of the elbows and knees, and in infants, the face and scalp.
- Small, raised bumps, which may leak fluid and crust over after scratching.
- Thickened, cracked, scaly skin.
- Raw, sensitive, swollen skin from scratching.
What causes eczema?
While the exact cause of eczema remains unknown, it is believed to be driven by a combination of genetic and environmental factors. People with eczema often have an overactive immune system that responds aggressively when triggered by allergens or irritants. Triggers include certain itchy materials, soaps and detergents, dust mites, pets, cold and dry air and certain foods. Stress and hormonal changes can also make it worse.
What are the 7 Different Types of Eczema?
Atopic Dermatitis
This type of eczema affects most people. Often starting in childhood, it shows up as itchy, red, swollen and cracked skin. It’s usually found on the face, inner elbows, behind the knees and on the hands and feet. This type is closely linked to asthma and hay fever, suggesting it’s strongly triggered by allergies.
Contact Dermatitis
This type occurs when the skin reacts to a substance it has come into contact with, causing localised inflammation.
There are two main types: irritant contact dermatitis, caused by chemicals or other irritants and allergic contact dermatitis, resulting from an allergen. Symptoms include redness, itching and sometimes sore blistering.
Dyshidrotic Eczema
Dyshidrotic eczema is marked by small, itchy blisters on the edges of the fingers, toes, palms and soles of the feet. It is more common in women and is associated with seasonal allergies or stress.
Nummular Eczema
Also known as discoid eczema, nummular eczema is notable for its distinct, coin-shaped spots of irritation that can be itchy and scaly. It can be triggered by a reaction to an insect bite or an allergic reaction to metals or chemicals.
Seborrheic Dermatitis
Seborrheic dermatitis mainly affects the scalp and face, particularly areas rich in oil-producing glands. It results in scaly patches, red skin and stubborn dandruff. Seasonal and hormonal changes may cause flare-ups.
Stasis Dermatitis
Stasis dermatitis occurs when poor blood flow in the lower legs leads to fluid leakage out of veins and into the skin, causing swelling, itching and pain. It is often seen in individuals with varicose veins or other circulatory conditions.
Neurodermatitis
Similar to atopic dermatitis, neurodermatitis leads to thick patches on the skin that look scaly. Typically confined to a few areas, it can be uncontrollably and intensely itchy. Stress can worsen the symptoms.
The Best Treatment for Eczema
- Regular moisturising
Moisturising with a thick, nourishing, fragrance-free lotion, like CeraVe or Aveeno, is the most important aspect of eczema treatment. Applying a moisturiser often will repair the skin barrier and reduce dryness, itching and inflammation. For severe dryness, ointments like petroleum jelly may be more effective than creams or lotions. Doing this will also help reduce scarring and improve any you may already have. - Topical corticosteroids
Prescription corticosteroid creams can reduce skin inflammation and flare-ups. They are available in various strengths and should be used as directed by a healthcare provider to avoid potential side effects, such as skin thinning. For mild eczema, low-potency steroids are usually sufficient, while more severe cases may require a higher level. - Calcineurin inhibitors
For individuals who do not respond well to steroids or who have long-term eczema, calcineurin inhibitors, such as tacrolimus and pimecrolimus, can be effective. These medications work by suppressing the immune system’s response that causes skin inflammation. They are particularly useful for treating sensitive areas such as the face and neck. - Biologic medication
Biologic meds, such as Dupilumab, are a newer class of treatment specifically designed for moderate-to-severe eczema that isn’t responding well to other treatments. Dupilumab targets a specific part of the immune system involved in inflammation, offering significant relief without some of the side effects associated with systemic corticosteroids. - Phototherapy
Those with eczema may find their symptoms improve in sunny climates. So, phototherapy, or light therapy, involves exposing the skin to controlled amounts of natural sunlight or artificial UV light can be beneficial for reducing symptoms of moderate to severe eczema, especially when other treatments have failed. - Lifestyle and home remedies
In addition to medical treatments, lifestyle changes can significantly impact eczema management. Avoiding triggers such as harsh soaps, detergents, wool clothing and certain foods can help. Regular bathing in lukewarm water followed by immediate moisturising can also alleviate symptoms. Stress management techniques, such as yoga and mindfulness, are shown to reduce flare-ups linked to stress. - Allergy management
Since allergies often exacerbate eczema, identifying and managing allergens is an important part of eczema treatment. Allergy testing can help pinpoint specific triggers, and avoiding these allergens or receiving allergy treatments can relieve irritating symptoms.
Take a Step Towards Healthier Skin Today
We encourage everyone dealing with eczema to stay informed, seek support and consult a dermatologist to explore the best possible strategies for managing their condition. Remember, with the right approach, eczema can be managed effectively, allowing you to lead a comfortable and fulfilling life.
Are you ready to take control of your eczema? Contact DermConsult today to schedule your personalised consultation. Let us help you find the best eczema treatment plan and bring relief to your life.

